

#Examples of autosomal dominant traits code#
Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Autosomal inheritance is a key component of Mendelian inheritance. DNA Types and Structure, originating from any 1 of the parents, into gametes. Mendelian inheritance is defined as a pattern of segregation of genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms.
#Examples of autosomal dominant traits pro#
Students: Educators’ Pro Tips for Tough Topics.Fundamentals of Nursing: Clinical Skills.That is a disease that is autosomal recessive does not necessarily mean the disease skips a generation. If the disease does skip a generation, then the disease is autosomal recessive. I imagine there’s a much better answer/way of saying this! – Luke Jul 5 ’12 at 11:29 Can a disease be autosomal if it skips a generation? When does a recessive trait skip a generation?Ī recessive trait may not skip a generation if the right mix of alleles are still passed to the progeny, but a dominant trait would always (by definition) be present in the offspring. Two people could have the exact same genetic mutation, but one might show no sign of it, while the other might be born with a cleft lip because of it.
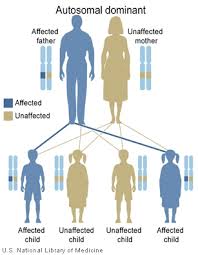
Sometimes a gene by itself isn’t “strong” enough to cause an effect 100% of the time. Here’s a few scenarios that may give the illusion of generation skipping. What are some examples of genes skipping generations? Autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive, multifactorial, and mitochondrial inheritance are examples. Mode of Inheritance is the manner in which a genetic trait or disorder is passed from one generation to the next. Which is an example of the mode of inheritance? If the disorder is dominant, one of the parents must have the disorder. Determine whether the disorder is dominant or recessive. If it is a 50/50 ratio between men and women the disorder is autosomal. How do you know if its autosomal dominant or recessive?ĭetermine if the pedigree chart shows an autosomal or X- linked disease.

Huntington’s disease and Marfan syndrome are two examples of autosomal dominant disorders. Which disease is an autosomal dominant disorder? The most common situation of an autosomal recessive disease occurs when the parents are each carrier or heterozygous (Dd). It is also common to see affected individuals with unaffected offspring. Can autosomal recessive traits skip generations?Īutosomal recessive patterns manifest by skipping generations as the affected are usually children of unaffected carriers. If the trait is displayed in offspring, at least one parent must show the trait. Patterns for Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Traits do not skip generations (generally). Which method of inheritance never skips a generation?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
